Most computers have virtualization features which ensure better performance in virtual machines, some of them are a virtual box, hyper-v, VMware and other.
With a Virtual machine software, you can run an entire operating system like Windows 10 or Ubuntu right from the current operating system. Suppose
Suppose if your computer is running on Windows 10 then you can emulate another Windows 10 instance in the virtual machine software. Then there are these other alternative operating systems as well as lightweight operating systems for old computers, Linux distributions, Ubuntu derivatives and Android operating systems. So you can grab an operating systems image file and boot it inside the virtual machine software to get it running. Sometimes to unlock the full performance these virtual machines require hardware acceleration features which are built into modern CPUs (such as Intel i3, i5 and i7). So when we talk about Intel CPUs it goes by Intel VT-x hardware acceleration and for AMD CPUs, it means AMD-V hardware acceleration.
If at some point you receive a message like saying “Oh, I can’t run this without the VT-x/AMD-c acceleration” or variants.
- VT-x/AMD-V hardware acceleration is not available on your system
- This host supports Intel VT-x, but Intel VT-x is disabled
- The processor on this computer is not compatible with Hyper-V
Try Uninstalling Hyper-V
Hyper-V is a feature included in the Windows 10 and unlike an installed app, uninstalling is not as simple as you might think.
Go to Control Panel > Uninstall a Program. In the “Programs and Features” window, click “Turn Windows features on or off.”
Control Panel\All Control Panel Items\Programs and Features
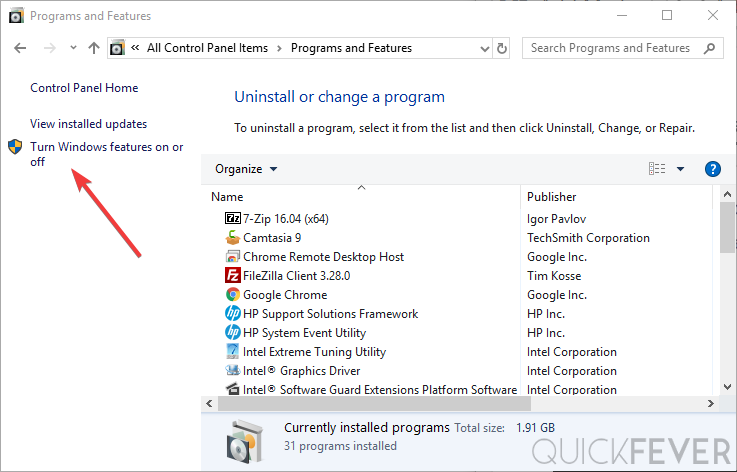
From the “Windows Features” box, untick the “Hyper-V” checkout and apply the setting. A restart is required before you try using a virtual machine again.
Enable Intel VT-x On in BIOS/UEFI Firmware
When you have an Intel CPU then you can enable the Virtualization feature (VT-x) from the BIOS settings. By default the option is disabled so you need to access the BIOS settings and turn on this feature, but remember this option is available in modern CPUs. Modern computers have UEFI firmware that allows a better solution for the low-level software which boots before your computer boots into the operating system with larger hard drive, more features and graphics and mouse cursor for convenience. PCs may also have both Legacy (BIOS) and UEFI boot support so you can access the BIOS settings and enable the VT-x feature and boot your computer again to use Virtual machine software and emulate guest operating system inside it.
On BIOS-based or Dual firmware PCs you need to access the BIOS settings
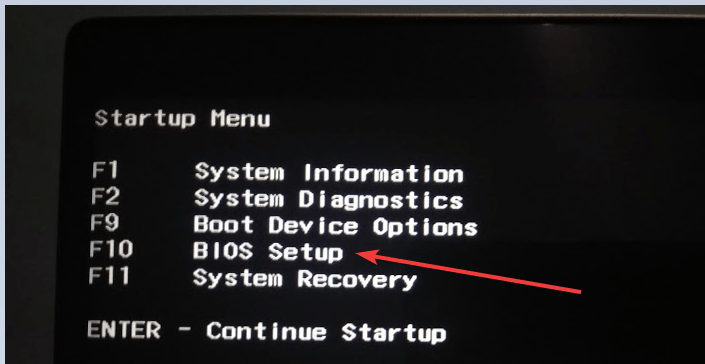
You need to access BIOS settings by restarting your computer and then hitting the “ESC” or “delete” or “F10” but it depends on your manufacturer’s preference, on HP laptop pressing the ESC key following by the F10 loads the BIOS settings. Pressing such key will eventually open the startup menu and from there press the appropriate key to load the BIOS settings. Sometimes, To access the BIOS settings, you ought to enter a default password but you can probably unlock it without any issues, but it’s more likely there is no default password on your laptop.
TIP: You might see something “Press {key} to access BIOS option” on the startup screen.
So eventually you have to go to BIOS settings and then advanced settings, on my HP laptop it’s under system configuration Goes by the name Virtualization Technology, select the option using the arrow keys and then press enter and from the menu select “enabled” then press the action key and save to save and exit the BIOS settings. When you open the virtual machine software by starting the computer next time, you can work without any scraps. You can smoothly run any operating system which requires visualization technology to be enabled on your computer.
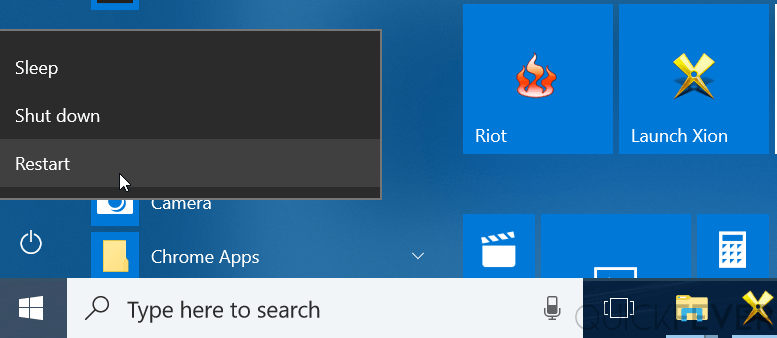
If you are running UEFI-based computer there is another way you can acces the firmware settings. For this to work you should be running on Windows 10 and logged into the operating system, hold down the Shift key and click the Restart button from the start menu.
Now from the advanced options, select the “UEFI Firmware Setting” and it will boot you into the Settings from where you’ll have to find and enable the virtualization feature (VT-x).
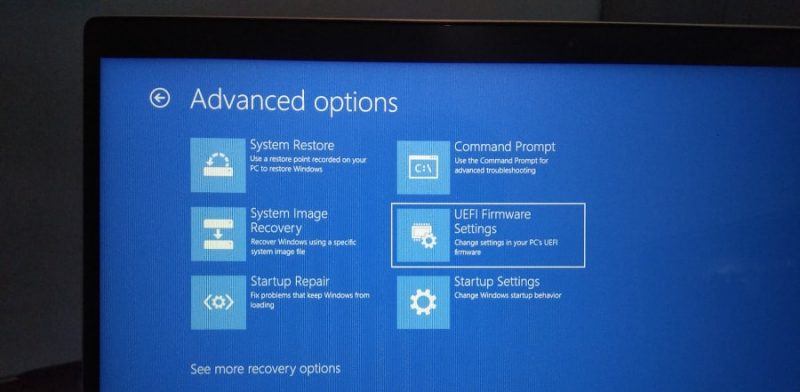
When you boot into UEFI settings sneak around and look for one of these “Intel VT-x,” “Intel Virtualization Technology,” “Virtualization Extensions,” or even “Vanderpool,” but if you can’t find it maybe you’ll have to live with that.
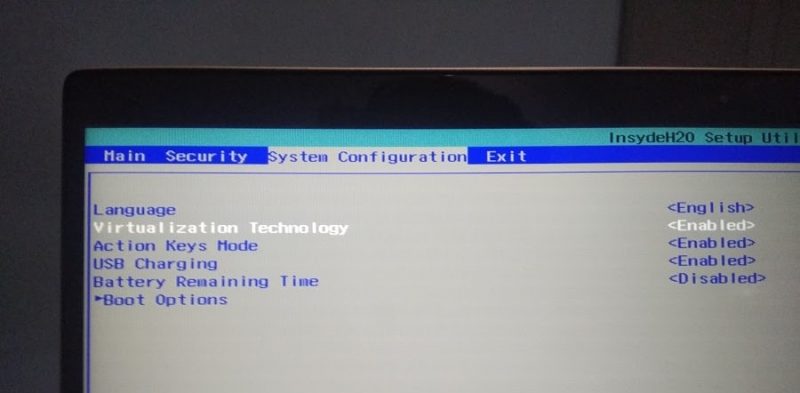
Once you find and enable the virtualization feature you can save and exit from the BIOS or UEFI settings and reboot PC to take effect.
After the PC restarts, you can try using VirtualBox or VMware again.
If You Don’t See the Intel VT-x Option
Unfortunately, not all the PCs includes this option in BIOS or UEFI settings, in that case, do a web search with the model number of your laptop, maybe there is a solution for a niche community.



1 comment
Found it on my BIOS. Thanks for the help!
Comments are closed.